Valve positioners are utilized on controlling valves where accurate and rapid control is needed without error or hysterises.
Positioners are usually mounted quietly-yoke or top casing from the pneumatic actuator for straight line sliding stem control valves, and also atOrclose to the finish-of-shaft for rotary control vales.
For either fundamental design type, “mechanical feedback linkage” connected straight to the valve’s stem provides feedback to controller.
The procedure controller informs the positioner to “change” squeeze feedback linkage reports to the positioner confirming that the change has happened and provides a “sense” from the magnitude from the alternation in position.
Principle of Operation
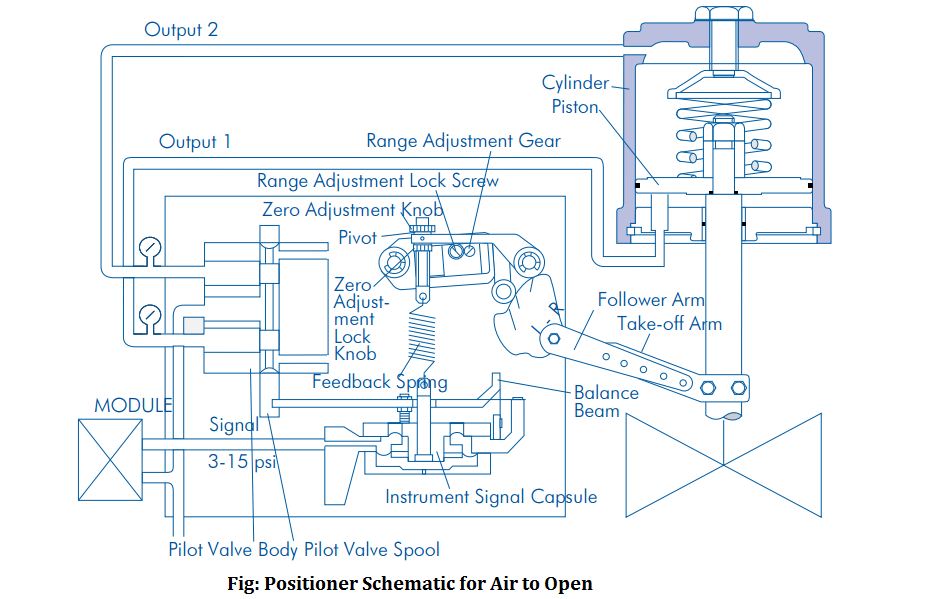
The Figure shows a valve positioner . The valve positioner is really a pressure-balanced instrument, with pneumatic module placed on a dual-acting actuator for air to spread out action. Positioning is dependant on an account balance of two forces one proportional towards the instrument signal and yet another proportional towards the stem position.
A downward pressure is activated because the signal pressure functions upon the diaphragms within the instrument signal capsule, with the follower arm and cam, the motion from the actuator stem is transmitted to the peak finish from the feedback spring inducing the different of hysteria in feedback spring as stem position changes.
The machine come in equilibrium and stem come in the positioning known as for through the instrument signal when these opposing forces balance exactly. The total amount will progress or lower and by way of the spool valve, can change the output pressures and flow rate if these opposing forces aren't in balance.
This can result in the piston to moving before the tension around the feedback spring opposes precisely the instrument signal pressure.
Control Valve Positioner Working Principle
The detailed sequence of positioner operations are listed below :
A rise in the instrument signal forces the instrument signal capsule and balance beam downward.
This motion from the balance beam also pulls the pilot valve spool downward from the equilibrium position.
This opens the pilot valve ports, offering air to port 1 and exhausting air from port 2.
This will cause the actuator piston upward. Proportionally towards the valve position, to counter the pressure generated through the instrument signal capsule, the piston is constantly on the stroke upwards until pressure within the feedback spring increases sufficiently.
At this time the total amount beam and spool begin to go back to equilibrium position.
Because the valve spool ports begin to close, the ventilation rate towards the actuator is decreased.
The feedback spring tension pressure will equal the pressure generated within the instrument signal capsule following the piston has arrived at the needed position.
The total amount beam and instrument signal capsule will stay within their equilibrium positions without any air flowing towards the actuator until a general change in the instrument signal is created.
A proportional downward movement from the actuator piston and stem is impacted by home loan business the instrument signal which reverses the described actions.
Control Valve Positioner Assembly
A valve positioner includes a high gain amplifier- this can be pneumatic, electro-pneumatic etc, along with a feed backlink which detects the particular position from the valve.
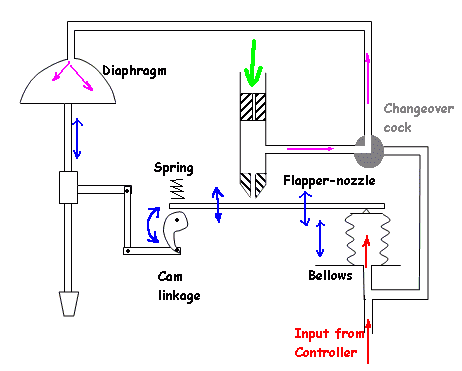
The needed movement is perfect for the valve to close. The input pressure in the controller towards the bellows falls. The flapper moves from the nozzle and also the pressure following the hole falls.
Pressure towards the diaphragm falls and also the valve starts to close. The feed back arm rises rotating the cam clockwise. This enhances the beam growing back pressure within the nozzle until equilibrium is again achieved.
The modification over cock enables the signal in the controller to become placed on the diaphragm
Valve Positioner Advantages
Precise positioning
can deal with large variations in forces functioning on plug
Rapid positioning
Removes stiction and friction results of gland
Removes results of large distances between valve and positioner
Eliminates hysterises
When should a positioner be fitted
A positioner should be thought about within the following conditions:
When accurate valve positioning is needed
To hurry in the valve response. The positioner uses greater pressure and greater ventilation to regulate the valve position
To improve pressure that the particular actuator and valve can close against. (To do something being an amplifier)
Once the valve pressure drop at it's peek operating flowrate, exceeds 5 bar for single sitting down valves or 10 bar for double sitting down valves
To linearize a non-straight line actuator
Where different differential pressures inside the fluid would make the plug position to alter
When controlling with wide throttling range and
When valves are handling sludge or solids in suspension.
