HISTORY & MYSTERY OF TRIPLE OFFSET BUTTERFLY VALVES

Today, TOVs offer numerous advantages to them, and many lately they have received attention due to the role they are able to play in managing fugitive emissions. The has begun to consider more unique and innovative methods for combating this global emissions challenge, and TOVs is a place where valve manufacturers have lately focused. By new and improved features, TOVs are utilized with techniques nothing you've seen prior seen while they're also getting used more cheaply. To know what lengths these valves came, we first must inspect the conventional benefits and features that made the TOV valuable, to begin with.
DECONSTRUCTING THE TOV
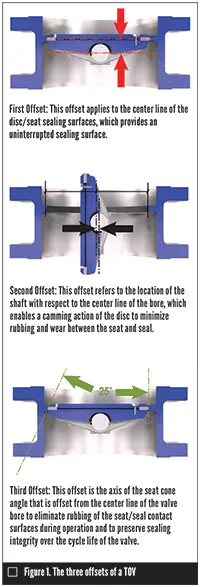
TOV could possibly be the right solution whenever a tight seal is needed. As it would seem, three separate offsets are made into the valve (Figure 1). They're: 1) the middle type of the disc/seat sealing surfaces, 2) the position of the shaft with regards to the center type of the bore, and three) the axis from the seat cone position that's offset in the center type of the valve bore.
The mixture of those three offsets offers an uninterrupted sealing surface, minimizes put on between your seat and seal, and preserves sealing integrity within the lifecycle from the valve. Furthermore, the enhanced seat position minimizes sticking or binding from the disc and lowers valve operating torque.
Generally, TOVs are selected for particular applications due to their sealing features in addition to financial savings over other metal-sitting down valve types. Due to the compact, quarter-turn design and light-weight structure, TOVs could be installed and operated easily, plus they require less pipe bracing. A replaceable seal ring that enables fast and simple repair and also the low torque of TOVs (which allows smaller sized actuators) mean much more financial savings.
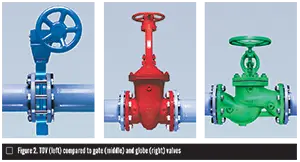
In accessory for the financial benefits, TOVs provide a bi-directional zero leakage closure having a metal seat once only accessible with soft-sitting down valves. This expands application options tremendously. Innovative self-centering, flexible seal rings and optimal torque transmissions mean these valves can provide fire-safe design and sealing performance that may be more than the biggest temperature selection of general butterfly valve designs (Figure 2).
Their use within all industries has elevated as strict government rules and greater production demands have compelled users to find solutions which are as efficient because they are effective. Usage can also be climbing since the options that come with the TOV which have been around for many years offer benefits to any or all applications, including individuals with greater challenges. A number of individuals benefits include operational efficiency, potential to deal with abrasive media and chemicals up to and including certain temperature or pressure, and flexibility within numerous operating conditions.
Taking advantage of previous TOV design features, generation x offers features that further enhance valve safety and feature, -including:
1. Metal-to-Metal Sealing. By providing a precision-machined metal seat and seal ring, the TOV delivers reliable and bi-directional shutoff approaching zero in high-temperature, high-pressure and severe service applications and more. Furthermore, the metal-to-metal seat can better handle thermal fluctuations, and also the standard right-position conical style of the TOV facilitates low-friction, in-line sealing, an essential feature in high-temperature/high-pressure applications. In hydrocarbon service, the metal-to-metal seat enables a valve to satisfy the requirement of fire-safe applications, that is further based on the TOV's quarter-turn characteristic.
2. Enhanced Seat Position. The seat position design coupled with using Stellite within the valve body seat, produces a longer seal existence, in addition to improved abrasion resistance, despite extensive cycling. This enhanced seat position can minimize wedging or binding from the disc, minimizing the operating torque.
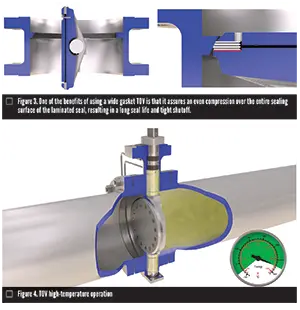
3. Torque seating. Torque-seating in TOVs enables the valve to self-adapt to evenly distribute seal compression. A “floating” seal ring along with a wide seal ring-supporting gasket yield an excellent seal along with a tight shutoff (Figure 3). A small rise in torque yields a much better seal due to more distributed compression from the seal ring across the entire sealing area. The applied torque also ensures a bi-directional seal.
4. Shaft Design. Positioning the pin connector within the lower area of the disk enables good performance in thermal expansion and minimizes shaft deflection, thus permitting an extended valve existence.
TRADITIONAL TOV AND UPDATED TRENDS
Today, manufacturers are tweaking the classic design and therefore are blending standard features with new ones which are enhancing TOV abilities, allowing these valves to focus on tougher applications and environments. TOVs will also be offered in an expanded size and pressure ranges. A vital differentiator from previous designs is really a tighter ISO Class A emissions level that typically was connected with bellow-sealed valves. By new stem seals, TOVs can provide fugitive emissions control under thermal cycling. This tighter seal can be done due to updated stem seal designs and be packing set up methods, which permit the valve to manage greater temperatures (Figure 4).
By providing different packing solutions, including standard process industry (ISO 15848, Class BH), a minimal-E option (ISO 15848, Class AH), and TA-Luft (VDI 2440), TOVs could be customized by the application.
Using the incorporation of those new kinds of features, TOVs can hold high-temperature steam applications, emergency shutdown service, and fire-safe applications.